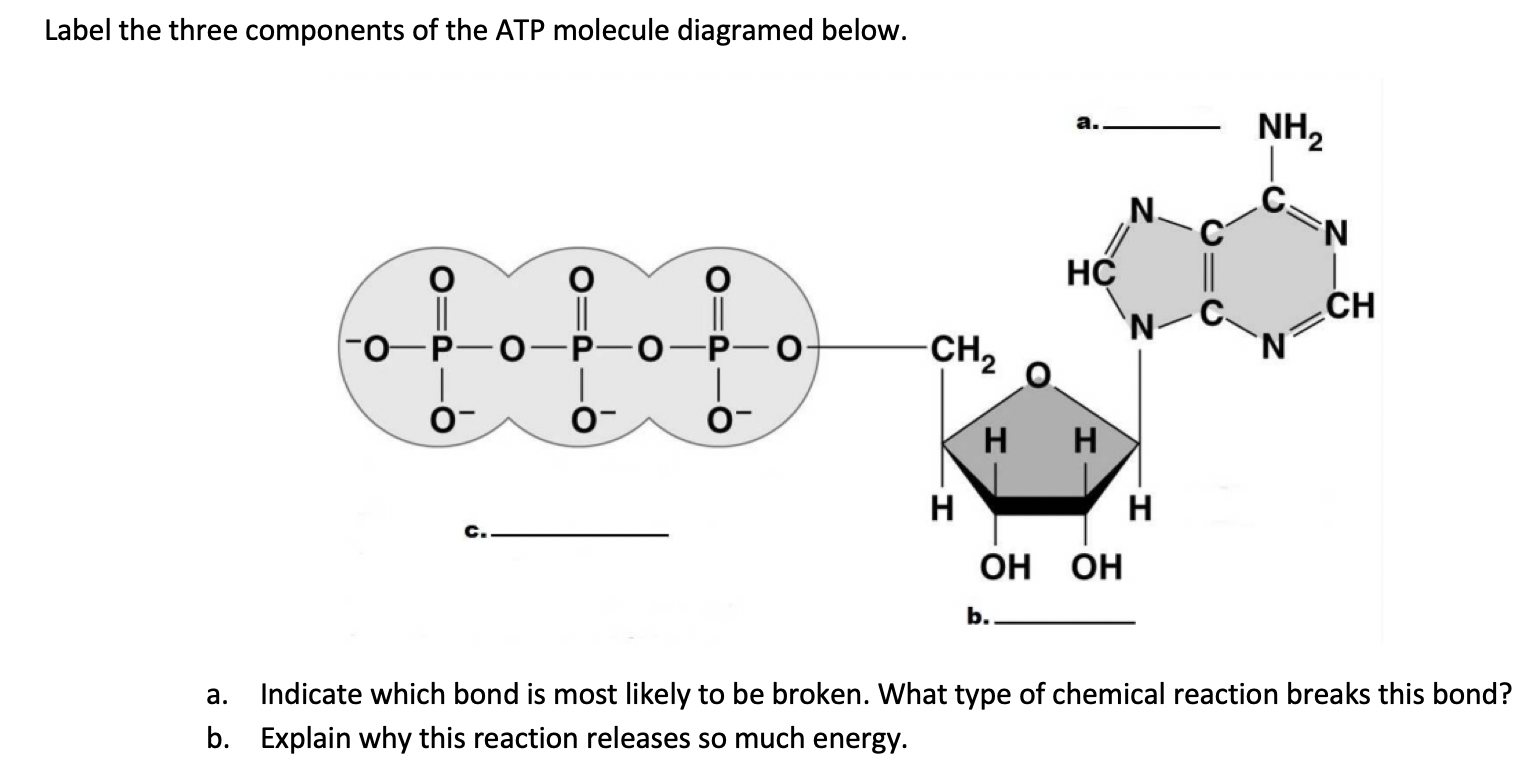
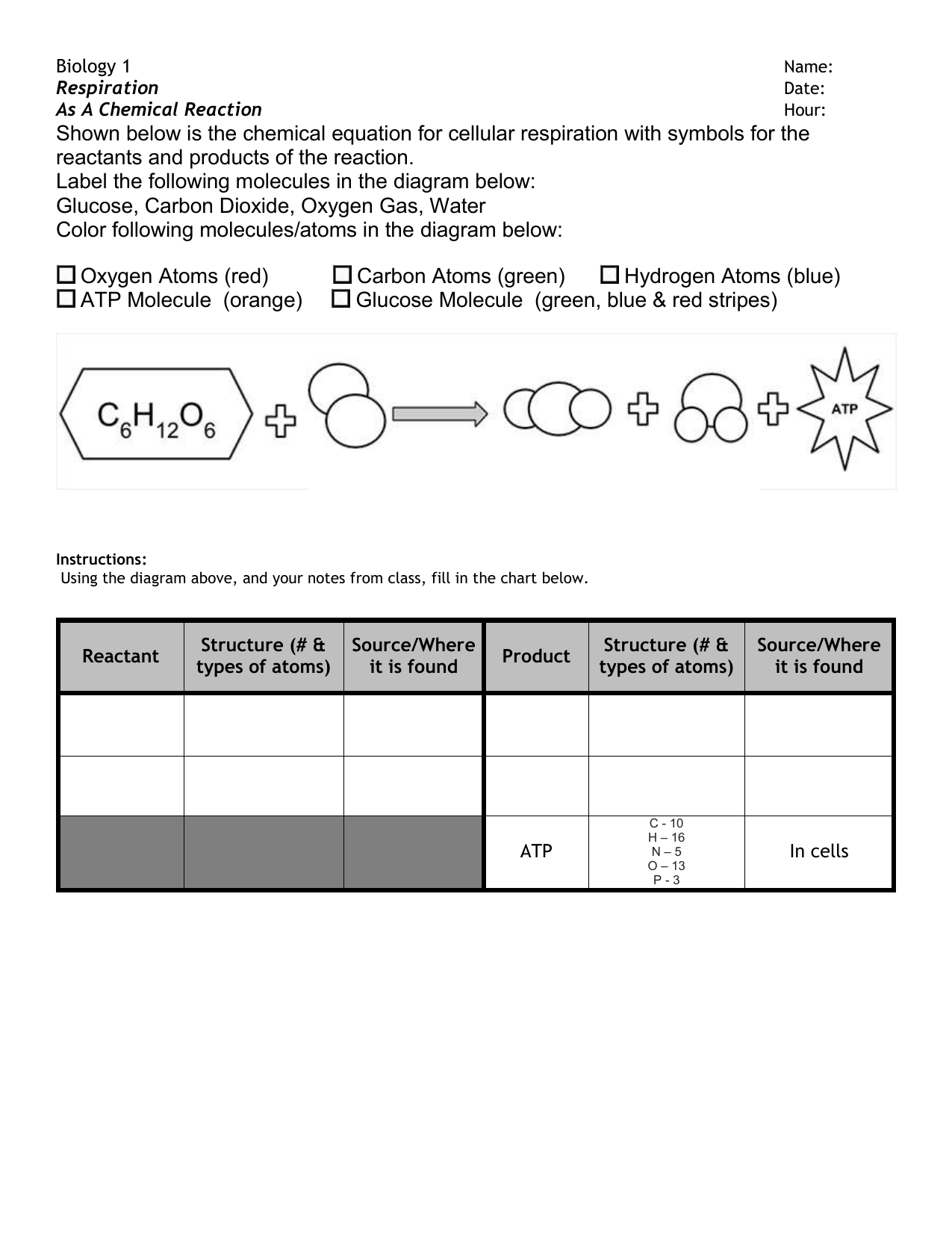
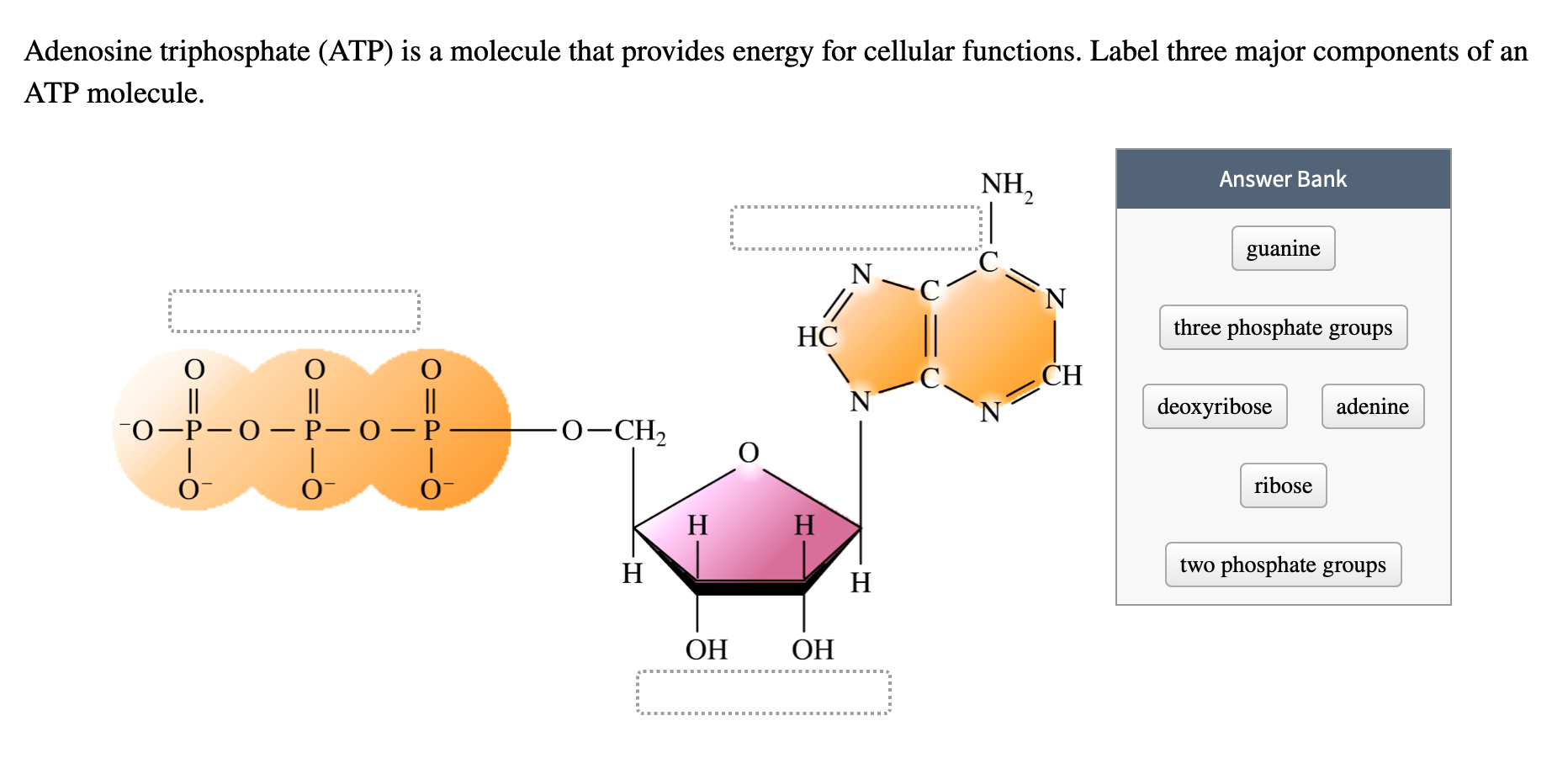
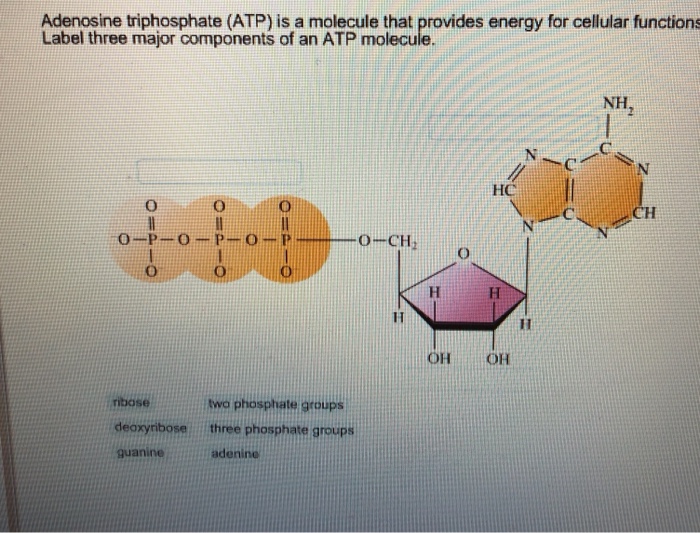
42 label the atp molecule below
DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Helicase - Wikipedia One label is a fluorescent lanthanide chelate, which serves as the label that is monitored through an adequate 96/384 well plate reader. The other label is an organic quencher molecule. The basis of this assay is the "quenching" or repressing of the lanthanide chelate signal by the organic quencher molecule when the two are in close proximity – as they would be when the DNA …
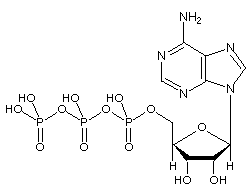
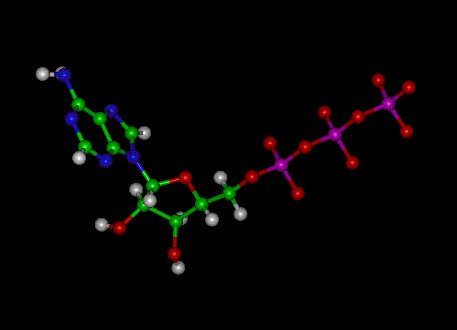
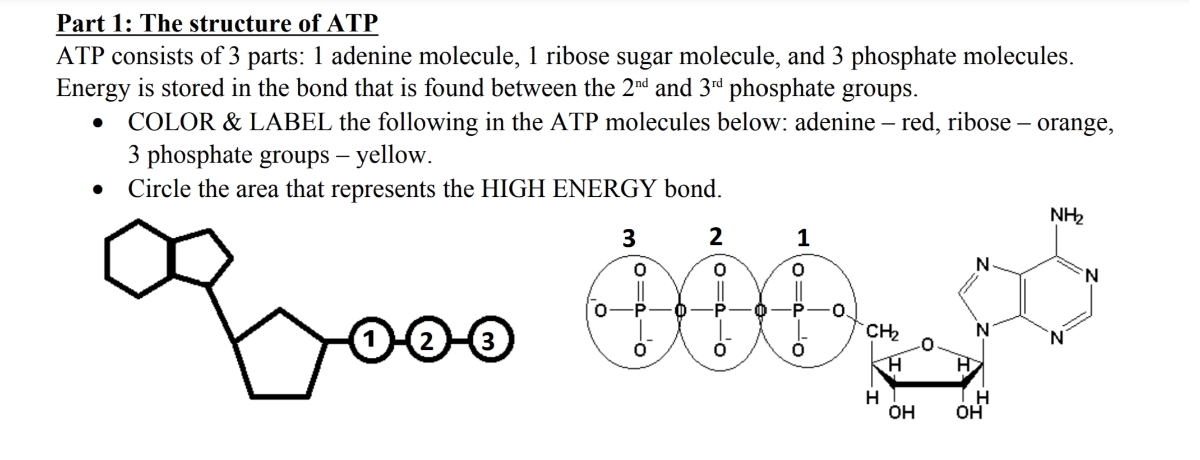
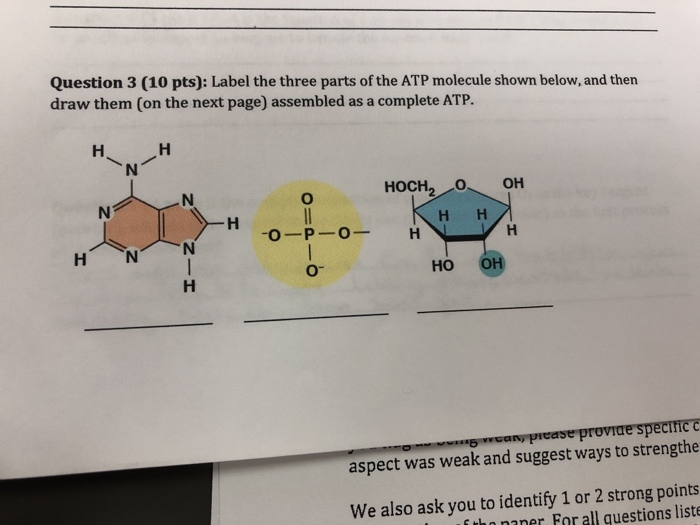
Answered: Part 1: The structure of ATP TP… | bartleby Part 1: The structure of ATP TP consists of 3 parts: I adenine molecule, I ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. nergy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. 1. COLOR the following ATP molecules below and provide a key to show the 3 parts. 2. Label the area that represents the HIGH ENERGY bond.
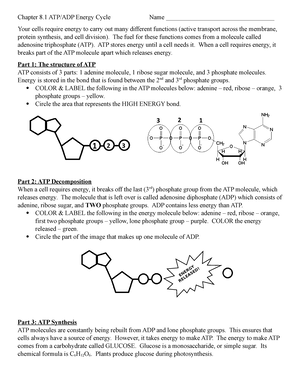
Label the atp molecule below
DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Helicase - Wikipedia With the use of specialized mathematical equations, some of these assays can be utilized to determine how many base paired nucleotides a helicase can break per hydrolysis of 1 ATP molecule. Commercially available diagnostic kits are also available. One such kit is the "Trupoint" diagnostic assay from PerkinElmer, Inc. This assay is a time ... PDF Name: KEY - mrsslovacek.weebly.com 3. Color and label the matrix yellow. Mitochondria Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by all cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar, and 3 phosphate groups. ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells.
Label the atp molecule below. Unit 6 Flashcards | Quizlet Label the coronal view of the head based on the hints provided. ... If four new drugs were discovered and each of them esulted in the unique physiologic responses indicated below, which drug do you think would hold the most promise as a cure for ... How many molecules of ATP are produced during one circuit of the Krebs cycle? 1. The Krebs cycle ... Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The discovery of ATP was made by Karl Lohman (1929). ATP is a nucleotide consisting of a base-adenine, a pentose sugar-ribose and three phosphate groups. Out of three phosphate groups the last two are attached by high energy rich bonds (Figure 14.3). On hydrolysis, it releases energy (7.3 K cal or 30.6 KJ/ATP) and it is found in all living ... PDF worksheet chemical energy and ATP - SC TRITON Science Identify the parts of an ATP molecule below: (Label adenosine, ribose, ... What happens to the ATP molecule when a phosphate group is removed ? (what does it turn into?) 8. Draw a diagram below showing the cycle of ATP and ADP below (see Figure 4.2 on page 101) 9. What type of organic compounds store the most energy? PDF Energy and ATP Packet - Ms. Bagherzadeh's Biology and A&P Web II Identify the parts of an ATP molecule below: (Label adenosine, ribose, and phosphate molecules) P 6. How is energy stored in the ATP molecule? p 7. What happens to the ATP molecule when a phosphate group is removed? (what does it turn into?) Generated CELL ATP: Use each of the belay just once to complete the passage. by
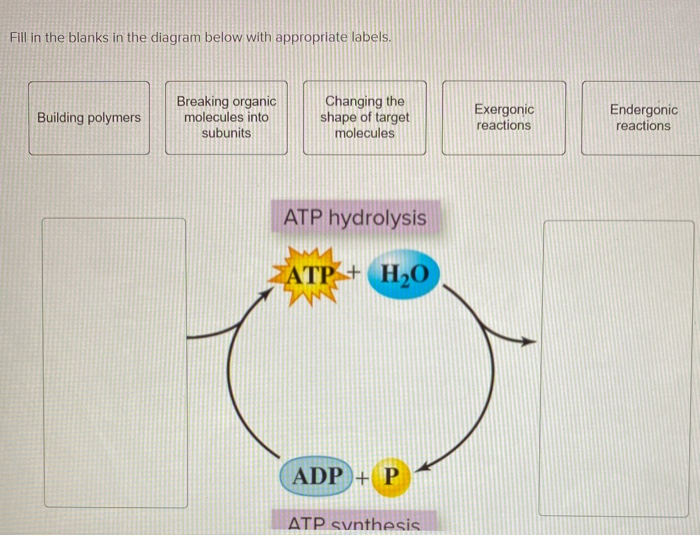
Ch. 5 Photosynthesis - Q Flashcards | Quizlet ATP and carbon dioxide. ATP and sunlight. ... Include the molecule preceded by a number. ... Drag the below phrases, which relate to photosynthesis, to the reaction category to which they best fit. Each label can be used only once and should be placed in only one category. PDF AP BIOLOGY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES - College Board ATP and GTP are primary sources of energy for biochemical reactions. (a) Describe the structure of the ATP or the GTP molecule. (1 point each; 2 points maximum) ... An energy pyramid for a marine ecosystem is shown below. Label each trophic level of the pyramid Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6. Total number of ATP molecules ENERGY COLOR LABEL the following in the energy molecule below adenine ... Part 4: ATP/ADP Cycle SEE CUT OUTS Label ATP and ADP molecules Label Adenine, Ribose, Phosphate Groups (1, 2, 3) both on the ATP & ADP molecule Color entire ATP GREEN Color Energy Released ORANGE Color Lightning Bolt PURPLE Color Lone Phosphate in ADP YELLOW Color entire ADP BLUE Color Energy Absorbed RED Cut all 4 images and rearrange them on the back of this worksheet showing the ATP/ADP cycle.
PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, TE - Scarsdale Public Schools Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples DOC Read, Answer, Color, Label: Mitochondria - New Smyrna Beach High School Color and label. the matrix (10) yellow on Figure 3. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a . nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine), a . 5-carbon sugar, and . 3 phosphate groups. ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. DOCX Ms. Grant's Bio Site - Home ATP consists of 3 parts: 1 adenine molecule, 1 ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. Energy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. COLOR & LABEL the following in the ATP molecules below: adenine - red, ribose - orange, 3 phosphate groups - yellow. atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace atp molecule labeled. This repair can result in a crossover (CO) or, more frequently, a non-crossover (NCO) recombinant. Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. What is atp an abbreviation for. n V (Ed. [6]
DOC Test: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration - Mrs. Murray's Honors ... 4. Label the ATP molecule below. 5. Look at the figure above. All of the following are parts of an ADP molecule EXCEPT _____ 6. In the figure above, between which parts of the molecule must the bonds be broken to form an ADP molecule? Photosynthesis. 7. Jan van Helmont concluded that plants gain most of their mass from _____. 8.
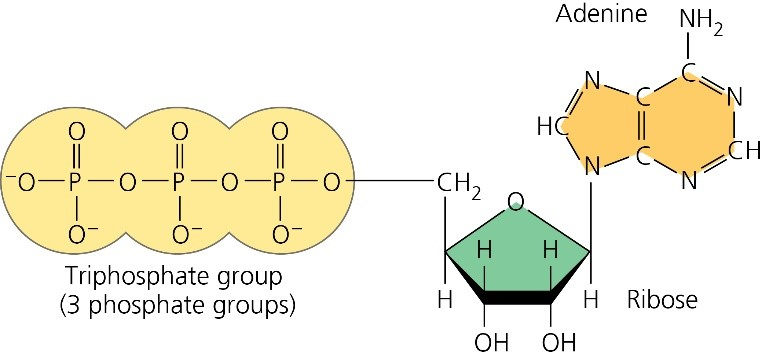
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture: Answer link.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
Insights into the client protein release mechanism of the ATP ... May 20, 2022 · To model the PRE spin label, an MTSL molecule was attached to the N-terminal cysteine residue. The resulting proteins were simulated with the ff14SB force field. The force field parameters of the ...
Unit 6 Flashcards | Quizlet Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify whether the structure is an actual part of the digestive tract or an accessory structure. Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify whether the structure is associated with the large or small intestines.
Solving Hardy Weinberg Problems - YouTube Paul Andersen shows you how to solve simple Hardy-Weinberg problems. He starts with a brief description of a gene pool and shows you how the formula is deri...
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate is an organic compound and hydrotrope that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate or to adenosine monophosphate. Other processes regenerate ATP s
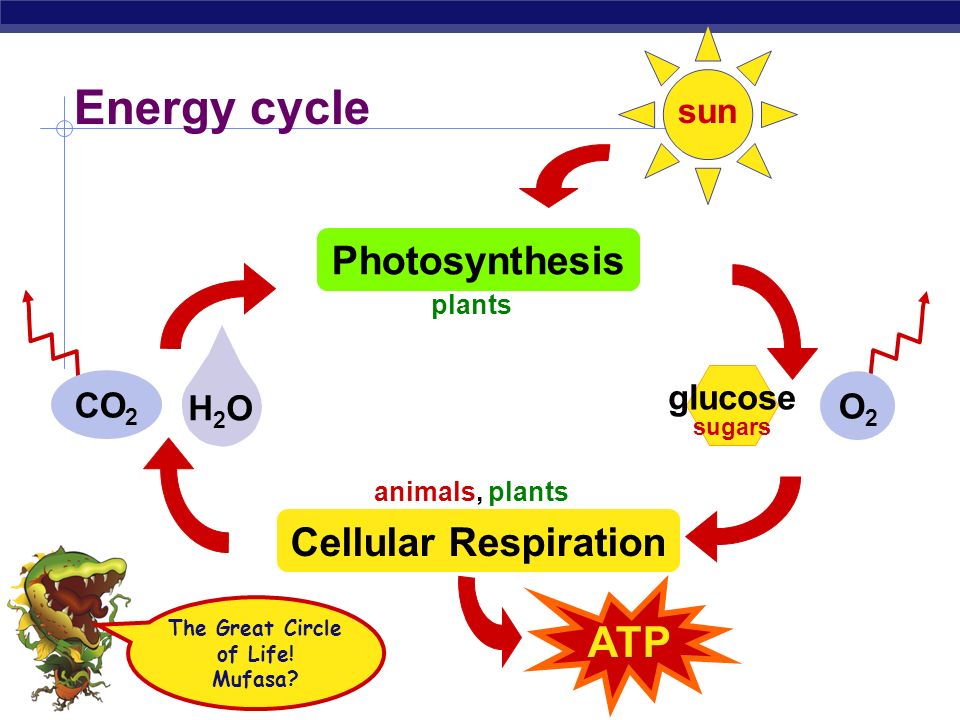
Learn About the 3 Main Stages of Cellular Respiration - ThoughtCo 06.05.2019 · We all need energy to function, and we get that energy from the foods we eat. Extracting those nutrients necessary to keep us going and then converting them into useable energy is the job of our cells.This complex yet efficient metabolic process, called cellular respiration, converts the energy derived from sugars, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into …
biology honors: chapter 8 Flashcards | Quizlet stroma. true/false:all heterotrophs must eat food to get energy. true. true/false: autotroph do not need to eat food because they make food. true. true/false: the energy in food originally came from ATP. false: sunlight. true/false: the term photosynthesis means "pulling apart with light" in Greek. false: putting together.
PDF ATP and Energy: How do cells capture, store, and release energy? 1. Based on the model of the ATP molecule above, list the three parts of the ATP molecule and then label each on the simplified model of ATP shown below a. b. c. 2. The full name for an ATP molecule is Adenosine Triphosphate. Based on the model for ATP, what is meant by the "tri" in triphosphate? 3.
1. In the diagram below, what is not a part of an ADP molecule? A. a C and D are the parts of the molecule in which the bonds must be broken to release energy and create ADP and D is not a part of ADP molecule.. Third phosphate is not a part of ADP molecule because there are only two phosphate atoms in ADP molecule whereas three atoms of phosphate are present in the molecule of ATP.It is because between C and D, phosphate molecules are present.
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and ...
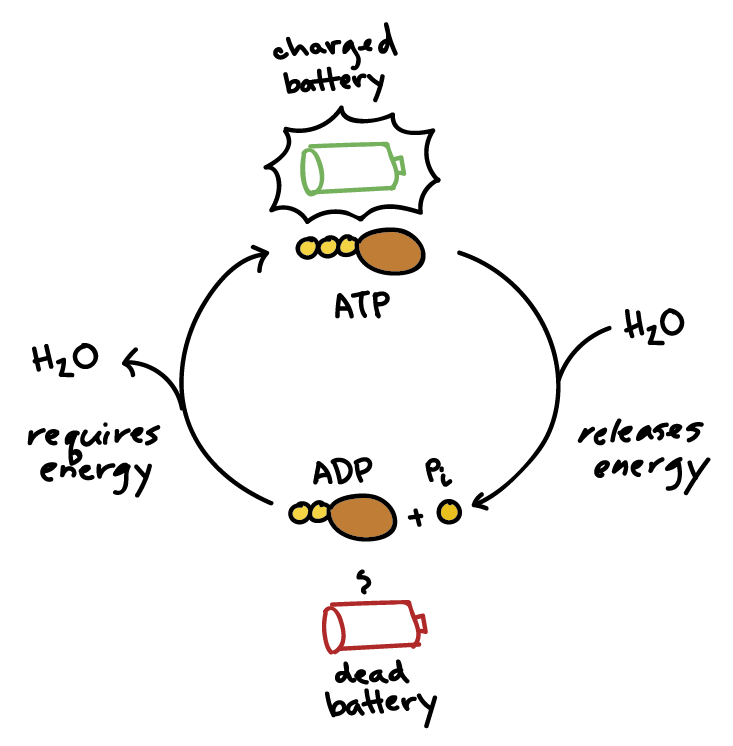
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule - Chegg The low battery represents an ADP molecule. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP results in loss of phosphate group. hence ADP + Pi is low energy state during ATP (energy carrier) …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below.
PharmaCircle This website uses cookies to help provide you with the best possible online experience. Please read our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy for information about ...
Learn About the 3 Main Stages of Cellular Respiration - ThoughtCo May 06, 2019 · ATP is ultimately produced by oxidative phosphorylation—the process by which enzymes in the cell oxidize nutrients. The protein ATP synthase uses the energy produced by the electron transport chain for the phosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule) of ADP to ATP. Most ATP generation occurs during the electron transport chain and ...
Solving Hardy Weinberg Problems - YouTube Paul Andersen shows you how to solve simple Hardy-Weinberg problems. He starts with a brief description of a gene pool and shows you how the formula is deri...
ATP Diagram | Quizlet ATP (name) adenosine triphosphate. ADP (name) adenosine diphosphate. ATP (function) a high energy molecule that transfers energy in cells. ADP (function) a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri.
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Insights into the client protein release mechanism of the ATP 20.05.2022 · How ATP-independent chaperones release ... The data points for Spy 1-124 CI R89D tends to be distributed below the diagonal ... To model the PRE spin label, an MTSL molecule was attached to the ...
SKELETAL MUSCLE ORGANIZATION - Brigham Young … Tropomyosin is a long string-like polypeptide that parallels each F actin strand and functions to either hide or expose the "active sites" on each globular actin molecule. Each tropomyosin molecule is long enough to cover the active binding sites on seven G-actin molecules. These proteins run end-to-end the entire length of the F actin.
PDF ATP - lcps.org List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. 2. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c. A sporting goods store might accept a $100 bill for the purchase of a bicycle, but the
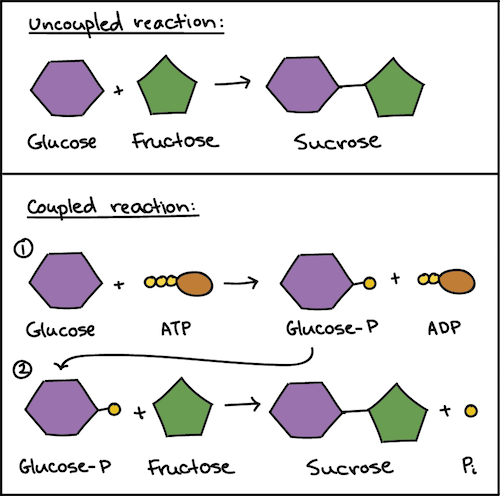
ATP AND BIOLOGICAL ENERGY - Estrella Mountain Community College This covalent bond is known as a pyrophosphate bond. We can write the chemical reaction for the formation of ATP as: a) in chemicalese: ADP + Pi + energy ----> ATP. b) in English: Adenosine diphosphate + inorganic Phosphate + energy produces Adenosine Triphosphate. The chemical formula for the expenditure/release of ATP energy can be written as ...
Model of ATP Molecule | Perkins eLearning The model described is of a molecule of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the energy currency of the cell because it provides energy for the cell's activities. Understanding the structure of this molecule leads to a clear understanding of the manner in which it provides needed energy to the cell. This model was created by Adele Hauser ...
PDF Photosynthesis (Chapter 8) Test Review - Ms. Schaller Science source)? __ATP___ Label the parts that compose this molecule: A: ___Adenine_____ B: 5-carbon sugar (ribose) *Notice it has 5 corners!* C: _____3 phosphate groups_____ 5.) Use the words: ENERGY STORING and ENERGY RELEASING to label what is happening in the reactions shown below: Breaking down ATP= ENERGY RELEASING
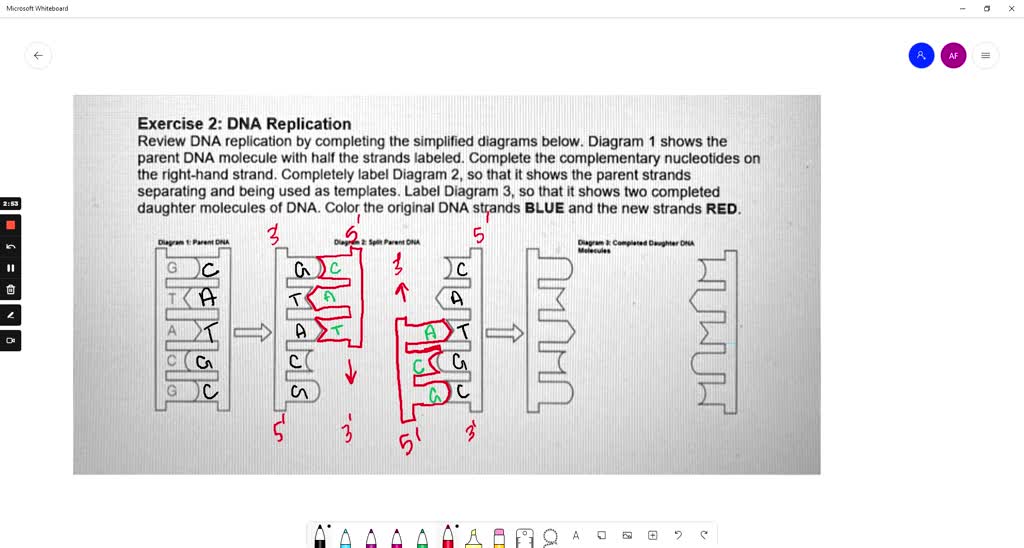
exercise 2 dna replication review dna replication by completing the simplified diagrams below diagram parent dna molecule with half the strands labeled complete the complementary nucleotides 86731
FANCJ Uses Its Motor ATPase to Destabilize Protein-DNA … 03.03.2009 · These results demonstrate that the M299I mutation exerts a gain-of-function effect on ATP-dependent streptavidin displacement activity, a result that is consistent with the elevated k cat for ATP hydrolysis of the M299I variant as well as its significantly increased helicase activity on duplex DNA substrates with backbone discontinuity obstacles that impede FANCJ-WT .
PharmaCircle This website uses cookies to help provide you with the best possible online experience. Please read our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy for information about ...
Part 2 atp decomposition when a cell requires energy The molecule that is left over is called adenosine diphosphate (ADP) which consists of adenine, ribose sugar, and TWO phosphate groups. ADP contains less energy than ATP. COLOR & LABEL the following in the energy molecule below: adenine - red, ribose - orange, first two phosphate groups - yellow, lone phosphate group - purple.
Answered: (i) Label the regions 1,2 and 3 in the… | bartleby Science Chemistry Q&A Library (i) Label the regions 1,2 and 3 in the ATP molecule given below as Phosphate, Base and Ribose (ii) Is this a 3' or 5' nucleotide? (iii) Is this a 2'-deoxy, 3'-deoxy or non-deoxy nucleotide?
PDF Name: KEY - mrsslovacek.weebly.com 3. Color and label the matrix yellow. Mitochondria Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by all cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar, and 3 phosphate groups. ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells.
Helicase - Wikipedia With the use of specialized mathematical equations, some of these assays can be utilized to determine how many base paired nucleotides a helicase can break per hydrolysis of 1 ATP molecule. Commercially available diagnostic kits are also available. One such kit is the "Trupoint" diagnostic assay from PerkinElmer, Inc. This assay is a time ...
DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA).


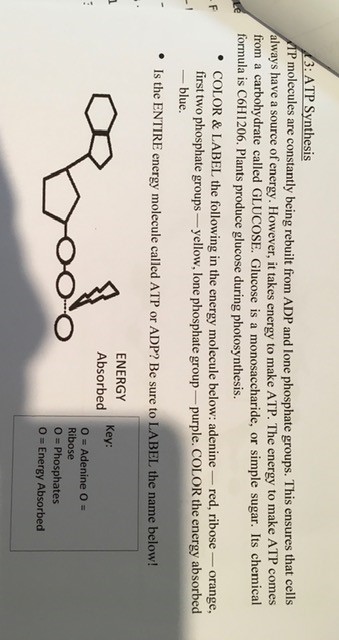













Post a Comment for "42 label the atp molecule below"